Drive System In motorcycles
Chain Drive:
Drive chains are most often made of metal, Conventional roller chain drives suffer the potential for vibration, as the effective radius of action in a chain and sprocket combination constantly changes during revolution.Virtually all high performance motorcycles use chain drive, with shaft driven arrangements generally used for many non-sporting machines. Toothed belt drives are used for many lower power motorcycles.
Shaft Drive:
A Drive shaft or Propeller shaft, is a mechanical component for transmitting torque and rotation, usually used to connect other components of a drive train that cannot be connected directly because of distance or the need to allow for relative movement between them.
Drive shafts are carriers of torque they are subject to torsion and shear stress, equivalent to the difference between the input torque and the load. They must therefore be strong enough to bear the stress, while avoiding too much additional weight as that would in turn increase their inertia.
Drive shafts frequently incorporate one or more universal joints or jaw couplings, and sometimes a splinned joint or prismatic joint to allow for variations in the alignment and distance between the driving and driven components.
A motorcycle has a motor mounted on a frame, a drive shaft extending from the motor transversely to the direction of travel, a rear wheel axle and a shaft drive mechanism extending longitudinally from the drive shaft to the rear wheel axle for transmitting power from the drive shaft to the rear wheel axle. The drive mechanism has an elongate housing with a first end portion mounted about the drive shaft and a second end portion mounted about the rear wheel axle. A drive gear is located on the drive shaft for rotation thereby, and an axle gear is located on the rear axle for driving the rear axle. A pinion shaft is supported by the housing so as to be rotatable about its own longitudinal axis. The pinion shaft has a front pinion gear meshing with the drive gear and a rear pinion gear meshing with the axle gear so that, when the drive shaft is driven by the motor, the force applied by the drive gear to the front pinion gear creates a first moment on the pinion shaft about the drive shaft which is opposite in direction to a second moment on the pinion shaft about the rear axle which is created by the force of the rear pinion gear driving the axle gear.
Belt Drive:
Belts are the cheapest utility for power transmission between shafts that may not be axially aligned. Power transmission is achieved by specially designed belts and pulleys. The demands on a belt drive transmission system are large and this has led to many variations on the theme. They run smoothly and with little noise, and cushion motor and bearings against load changes, albeit with less strength than gears or chains. However, improvements in belt engineering allow use of belts in systems that only formerly allowed chains.
The belt drives are commonly used in Harley Davidson motorcycles to give a better Cruising and Comfortable long rides - the main advantage of belt drives.
All three are valid and workable technologies. In addition, they’ve all been around a very long time. “Which is best” depends upon your type of riding and/or personal preference.
Stated briefly, chain drives are the most economical way to transmit power to the rear wheel. They also convey the greatest percentage of engine power in the process. Chain drives are by far the most popular drive mechanism in motorbikes around the world. On the other hand, they also require the most maintenance, are dirty, and not as smooth as a shaft or belt drive.
Hence, belt drives are a viable option where available (mostly, but not exclusively, on cruisers). Not only do belts require less frequent adjustments than a chain, they also last longer, so the whole task of having them replaced is reduced. Belt drives are cleaner since there is no chain lube flying around to mess up your bike or that belt in your jeans with gold chains and chrome, shaft pendants dangling around. Belt drives are also smoother than chain drives.
And finally, there are shaft drives: Shaft drives are smooth. They are the lowest maintenance of the three. (The shaft drive oil reservoir needs to be infrequently drained and replaced). They are quiet and clean. Motorcycle shaft drives are also heavier and more expensive than chain or belt drives. Furthermore, a small amount of performance is lost while moving that power from the engine to the rear wheel via some extra gears in the shaft drive. Hence, you won’t see them on pure performance machines.
The drive systems refer to the transmitting of power from the engine to the wheels. The commonly used drive system in motorcycles are
- Chain Drive
- Shaft or Axle Drive
- Belt Drive
Chain Drive:
Chain drive is a way of transmitting mechanical power from one place to another. It is often used to convey power to the wheels of a vehicle, especially motorcycles. It is also used in a wide variety of machines besides vehicles.
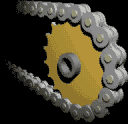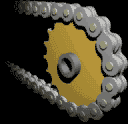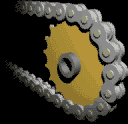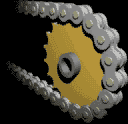 |
| The Chain & Sprocket |
Most often, the power is conveyed by a roller chain, known as the drive chain or transmission chain, passing over a sprocket gear, with the teeth of the gear meshing with the holes in the links of the chain. The gear is turned, and this pulls the chain putting mechanical force into the system. Sometimes the power is output by simply rotating the chain, which can be used to lift or drag objects.
 |
| The Chain & Sprocket In Yamaha R1 |
Drive chains are most often made of metal, Conventional roller chain drives suffer the potential for vibration, as the effective radius of action in a chain and sprocket combination constantly changes during revolution.Virtually all high performance motorcycles use chain drive, with shaft driven arrangements generally used for many non-sporting machines. Toothed belt drives are used for many lower power motorcycles.
 |
| Chain |
 |
| Sprocket |
Shaft Drive:
A Drive shaft or Propeller shaft, is a mechanical component for transmitting torque and rotation, usually used to connect other components of a drive train that cannot be connected directly because of distance or the need to allow for relative movement between them.
 |
| The Shaft Drive Train |
Drive shafts are carriers of torque they are subject to torsion and shear stress, equivalent to the difference between the input torque and the load. They must therefore be strong enough to bear the stress, while avoiding too much additional weight as that would in turn increase their inertia.
Drive shafts frequently incorporate one or more universal joints or jaw couplings, and sometimes a splinned joint or prismatic joint to allow for variations in the alignment and distance between the driving and driven components.
 |
| Shaft driven Motorcycle |
A motorcycle has a motor mounted on a frame, a drive shaft extending from the motor transversely to the direction of travel, a rear wheel axle and a shaft drive mechanism extending longitudinally from the drive shaft to the rear wheel axle for transmitting power from the drive shaft to the rear wheel axle. The drive mechanism has an elongate housing with a first end portion mounted about the drive shaft and a second end portion mounted about the rear wheel axle. A drive gear is located on the drive shaft for rotation thereby, and an axle gear is located on the rear axle for driving the rear axle. A pinion shaft is supported by the housing so as to be rotatable about its own longitudinal axis. The pinion shaft has a front pinion gear meshing with the drive gear and a rear pinion gear meshing with the axle gear so that, when the drive shaft is driven by the motor, the force applied by the drive gear to the front pinion gear creates a first moment on the pinion shaft about the drive shaft which is opposite in direction to a second moment on the pinion shaft about the rear axle which is created by the force of the rear pinion gear driving the axle gear.
 |
| Yamaha V Max Using the Shaft Drive |
Belts are the cheapest utility for power transmission between shafts that may not be axially aligned. Power transmission is achieved by specially designed belts and pulleys. The demands on a belt drive transmission system are large and this has led to many variations on the theme. They run smoothly and with little noise, and cushion motor and bearings against load changes, albeit with less strength than gears or chains. However, improvements in belt engineering allow use of belts in systems that only formerly allowed chains.
 |
The Belt Driven BMW F 800
|
 |
| Harley Davidson- Electra Glide Classic |
Chain? Belt? Shaft? Which is Better?
All three are valid and workable technologies. In addition, they’ve all been around a very long time. “Which is best” depends upon your type of riding and/or personal preference.
- However, most large touring bikes are usually equipped with a shaft drive
- Cruisers are the most popular type of bikes to find belt drives, although you can buy cruisers with shaft or chain drives
- Sport-touring bikes primarily include chain or shaft drives
- Most adventure-touring bikes are driven by chain or shaft with a rare belt-drive exception
Stated briefly, chain drives are the most economical way to transmit power to the rear wheel. They also convey the greatest percentage of engine power in the process. Chain drives are by far the most popular drive mechanism in motorbikes around the world. On the other hand, they also require the most maintenance, are dirty, and not as smooth as a shaft or belt drive.
Hence, belt drives are a viable option where available (mostly, but not exclusively, on cruisers). Not only do belts require less frequent adjustments than a chain, they also last longer, so the whole task of having them replaced is reduced. Belt drives are cleaner since there is no chain lube flying around to mess up your bike or that belt in your jeans with gold chains and chrome, shaft pendants dangling around. Belt drives are also smoother than chain drives.
And finally, there are shaft drives: Shaft drives are smooth. They are the lowest maintenance of the three. (The shaft drive oil reservoir needs to be infrequently drained and replaced). They are quiet and clean. Motorcycle shaft drives are also heavier and more expensive than chain or belt drives. Furthermore, a small amount of performance is lost while moving that power from the engine to the rear wheel via some extra gears in the shaft drive. Hence, you won’t see them on pure performance machines.
